what is
The weight of an adult's head can reach 3-5 kilograms: the skull weighs about 1400 grams, about the same weight as the brain, and the mass of blood circulating in the skull is about 500 grams.
Development reasons
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Compulsion to maintain tense postures while working (driving, in front of a computer);
- overweight;
- nervous state;
- neck injuries;
- Muscle weakness.
- genetic predisposition;
- Autoimmune diseases that cause cartilage tissue to degenerate;
- Congenital disorders of spinal development.
Stages and symptoms of pathological development
Stage 1. The symptoms remain virtually invisible. At this stage you can stop or slow down the pathological process without the help of drugs (diet, exercise). Patients may feel: - Discomfort, tension, and hardness of neck and shoulder muscles;
- Mild pain when turning or tilting the head;
- Headaches are infrequent and of low intensity (most commonly after static or strenuous work, stressful experiences).
second stage. The height of the intervertebral discs is reduced, the nerve endings are compressed, and severe pain occurs in the neck, especially when performing activities and turning. Muscle spasms disrupt the blood supply to the skull, thus increasing symptoms associated with vascular insufficiency. The person noted: - Creaking of neck joints when turning head;
- decreased vision;
- tinnitus;
- Dizziness;
- Frequent headaches with no apparent cause;
- Numbness of the face and neck, and loss of sensitivity of the skin on the hands and collar area;
- Severe pain radiating to the shoulder blade;
- sleep disorder.
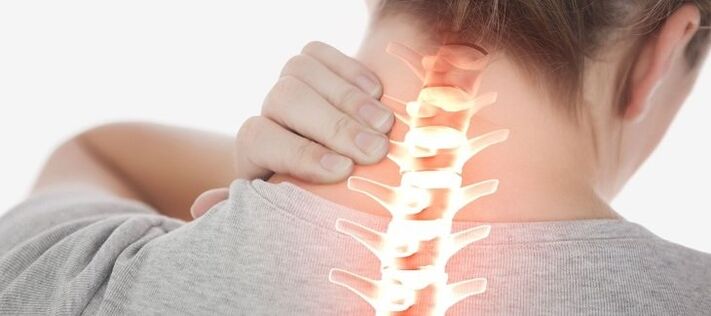
The third phase. A herniated disc develops (its core protrudes into the spinal canal), which can lead to nervous system dysfunction. Symptoms may include: - Numbness in the hands and possible paralysis of the upper limbs;
- Pain affects the entire neck and collar area and can radiate to the heart area;
- "Floaters" appear in the eyes, nausea and vomiting;
- Feeling of a lump or pain in your throat, such as sore throat;
- The skin of the upper body may not be felt at all;
- Dizziness can occur with almost any exercise;
- The headache is essentially a migraine.
Stage 4. It is characterized by complete disk corruption: - Tinnitus may be permanent;
- Dizziness may be accompanied by loss of consciousness;
- Coordination disorders occur when blood supply to the cerebellum region of the brain is reduced.
It is extremely rare for a single disc to be affected. Often the process involves the entire department. Individual disks may be in different stages of corruption.
diagnosis
- Radiography - will show changes in spinal structure, but in advanced stages of pathology;
- Computed tomography - shows changes in the vertebrae, but intervertebral hernia and spinal cord compression are difficult to differentiate;
- Magnetic resonance imaging - allows you to see the intervertebral hernia and the direction in which it is growing;
- Ultrasound duplex scan - shows blood flow velocity in areas of suspected osteochondrosis.
When doctors make a diagnosis, they base their diagnosis on the symptoms the patient is exhibiting. A syndrome is a combination of disease symptoms.
spine- Indicates that the pathological process involves bone and cartilaginous tissue. Checklist: - Limited neck movement;
- pain when turning the neck;
- Structural changes in the vertebrae or discs (shown on X-rays).
vertebral artery syndrome– means that the vertebral arteries, which supply blood to the brain, are involved in the pathological process. The main symptoms: Due to lack of blood circulation: - noise in ears;
- Dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- pressure fluctuations;
Due to stimulation of arterial nerve endings: - severe headache (migraine);
- Numbness of scalp skin;
- "Floaters" in the eyes or temporary blindness;
due to lack of oxygen; - faint;
- lethargy;
- Loss of ability to focus on anything;
- frustrated;
- Panic attacks.
heart.Signs similar to cardiovascular system problems: - Sternal pain (sometimes like a burning sensation);
- shortness of breath and fatigue;
- Increased heart rate.
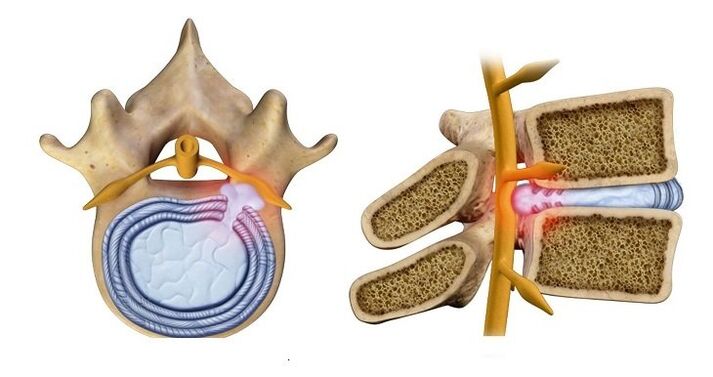
Koreshkovi.Associated with impaired conduction of nerve impulses, depending on damage to a specific pair of roots that innervate the neck region: - Root pair 1-2 - pain or numbness in the back of the head;
- The third pair - numb tongue, difficulty chewing food;
- The fourth pair - clavicle pain, lump in throat, difficulty swallowing food;
- Fifth pair - Difficulty moving the arms, the problem is concentrated in the shoulder area;
- Sixth Couple - Discomfort in the shoulder blade and forearm area;
- The seventh pair - numbness in the hands, more common in the middle and index fingers;
- The eighth pair - numbness of the ring finger and little finger.
Treatment programs
medical treatement
- relief the pain;
- Relieve inflammation and swelling;
- Reduce neck muscle tension;
- Improve blood circulation;
- Protects cartilage tissue from damage and promotes its repair.
To diagnose and treat cervical osteochondrosis, you should contact a neurologist. If the clinic has a chiropractor who directly deals with spinal conditions, you can contact him immediately.
- NSAIDs – Relieve inflammation and swelling and reduce pain.
- B vitamins – Help improve the function of nervous tissue.
- Chondroprotectants - protect cartilage tissue from destruction and restore its structure.
- Medications that improve blood flow.
- Muscle relaxants are medications that relieve muscle spasms.
physical therapy methods
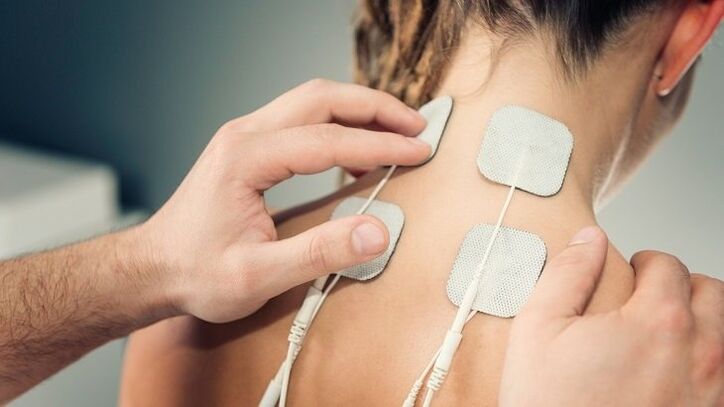
- electrophoresis– The affected area is exposed to low intensity electrical current. Delivers medication directly to problem areas. Anesthetics are usually used to relieve pain, or medications are given to improve blood flow to the neck area.
- ultrasound– Has anti-inflammatory properties, improves blood flow and metabolic processes.
- Magnet therapy– Helps to quickly relieve tissue swelling and improve metabolic processes.
- Laser Treatment– Helps improve blood circulation at the contact site and has anti-inflammatory properties.
massage
Self-massage can be used later, just be very careful not to try to repeat the depth of impact shown by a professional massage therapist.
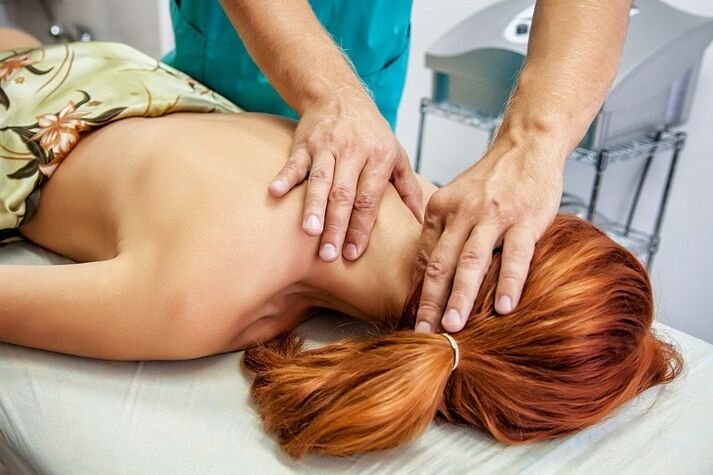
- Stroking - Activates the surface of the skin;
- Squeeze - connect the deep layers of the skin;
- Rubbing – warms and relaxes muscles and improves circulation;
- Kneading - affects very deep tissues, so use with caution;
- Vibration - Tapping and shaking ends the process.
manual therapy
- There is no doubt that a chiropractor must be a highly qualified doctor with medical education and qualifications as a neurologist or orthopedic traumatologist.
- There are many contraindications to manual treatment of cervical osteochondrosis. Two people with similar symptoms may get different answers as to whether they need manual therapy—one can and should, the other definitely not.
A highly qualified chiropractor will not treat a patient without studying the x-ray results.
treatment at home
Therapeutic exercise (physical therapy)
Patients should not feel pain while performing the exercises. Doing it "with pain" not only has no benefit, but will harm your health.
saint collar
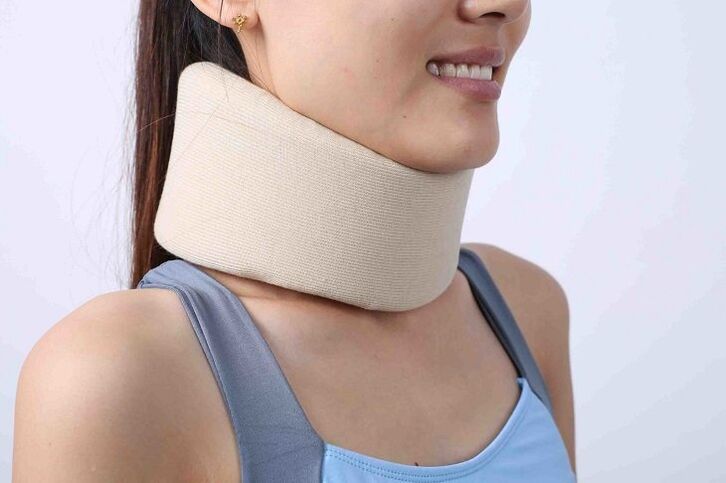
If 5-7 cervical vertebrae are unstable, bandages cannot be used as they will not be held in the correct position. It is also not recommended to wear a collar if the thyroid gland is enlarged.
Application of orthopedic pillow
prevention
- Monitor your weight; 10kg over the standard can severely load the entire spine;
- Try not to lift or carry heavy objects;
- If you need to carry a heavier bag, hold it alternately with your left and right hands (or better yet, use a backpack that distributes the load evenly across your entire back);
- Every half hour of static work should be alternated with light exercise to relieve muscle tension and improve blood circulation;
- Engaging in sports such as swimming is beneficial, but running, jumping, weightlifting, etc. are harmful to the spine;
- When sleeping, use an orthopedic mattress and pillow.